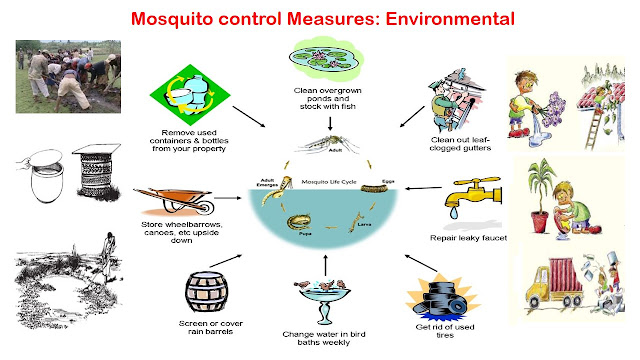
Spotters in "Environment and Health: Insecticides" for CFM & MPH students

Insecticides: These are substances that are used to kill insects. Pesticides: It is a general term that includes insecticides, fungicides rodenticides, herbicides, disinfectants, repellents, and other chemicals used for the control of pests. Insecticides are classified into 3 groups: Contact poisons, Stomach poisons and Fumigants. CONTACT POISONS: These are those insecticides that kill insects primarily by contact e.g., pyrethrum, DDT, HCH, dieldrin. STOMACH POISONS: These are those insecticides which when ingested cause the death of the insects, e.g., Paris green, sodium fluoride. FUMIGANTS: These are those insecticides that give off vapours that have a lethal effect on the insects, e.g., sulphur dioxide. 1. DDT (Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane) : It was first synthesized in 1874, by a German chemist, Ziedler . I ts insecticidal properties were discovered by the Swis...