Diabetes : Lets learn how to inject insulin
What is the need?
The
proper injection of insulin is very important to allow the body to function normally hence we should be very strict
about the way we manage the insulin injections.
Common mistakes done:
- Poor mixing technique when mixing insulin.
- Wrong doses (because of poor eyesight).
- Poor injection technique—into the skin or muscle rather than the soft, fatty layer.
- Not taking insulin when you feel ill.
When to inject insulin?
Develop
a set routine, including eating your meals on time and giving the injections
about 30 minutes before your meal
Where to inject insulin?
The injection should go into the fatty (subcutaneous) tissue between the skin and muscle.
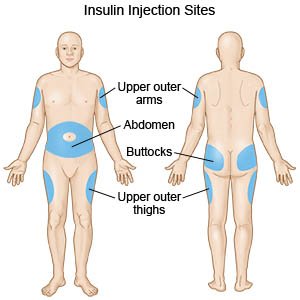
- Abdomen below the navel is the best place.
- Other suitable areas are the buttocks and thighs.
- These areas having a good layer of fat under the skin and are free of large blood vessels and nerves.
- It is advisable to stick to one area, and the abdomen is recommended.
- Avoid giving injections into the arms, near joints, the navel and the groin.
- Do not inject too often into the same small area (it can damage the tissue).
- Give the injection at a different place each time.
- Keep a distance of 3 cm (1½ inches) or more from the last injection.
How to inject insulin?
This depends on the insulin injection device; those in common
use are insulin syringes and insulin delivery pens. The techniques should be
explained to you by the doctor.
Insulin syringe method:
• Lift up or pinch a large area of skin on your abdomen between
your thumb and fingers.
• Hold the syringe in your other (dominant) hand between your thumb and middle finger: this leaves the index finger free to push the plunger. Breathe in and out.
• Insert the needle straight in (like a dart) at right
angles to the skin (push the needle well in but not into the muscle).
• Push the plunger all the way down.
• Quickly withdraw the needle.
• Press down firmly (do not rub or massage) over the injection
site for up to 60 seconds.
Drawing up the insulin:
Make sure your technique is checked by the doctor/an expert. You may
be using either a single insulin or a mixed insulin. A mixed insulin is a
combination of shorter- and longer acting insulin and is cloudy.
Rules for mixing:
• Always draw up clear insulin first.
• Do not permit any of the cloudy insulin to get into the
clear insulin bottle.
• Do not push any of the clear insulin into the cloudy insulin bottle
Drawing up rules:
• Wash and dry your hands beforehand.
• Gently roll the insulin bottle between your hands to mix—do
not shake it.
• Always draw up air equal to the dose of insulin into
the syringe.
• Always expel air bubbles and ensure that you do not inject
air.
Insulin delivery pen
Follow the instructions in the manual and according to
your educator:
• Screw a new needle tightly onto the cap.
• Perform an ‘air shot’ to expel bubbles of air.
• Dial the correct number of units.
• Insert the needle at 90° to the skin of the abdomen (or
thigh or arm).
• Push the button down fully to inject insulin into subcutaneous
tissue.

• Count slowly to 6 and withdraw.
• Remove the needle and discard it.
How to decrease pain?
- Always inject insulin at room temperature.
- If the insulin has been stored in the refrigerator, remove it 30 minutes before injection.
- Remove all air bubbles before the injection from the syringe.
- If you clean your skin with an alcohol, wait until it has dried before you inject insulin.
- Relax the muscles at the injection site.
- Never change the direction of the needle during insertion or removal.
Golden rules:
•
Take your insulin every day, even if you feel ill.
•
Do not change your dose unless instructed.
• Carefully dispose of used syringes and pen needles.
- John M. Murtaghs Patient Education. of 6th revised ed edition. North Ryde NSW: McGraw-Hill Australia. 2012
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
- https://www.cdc.gov/
- https://vikaspedia.in/health/diseases/diabetes/diet-and-diabetes
- https://www.drugs.com/cg/how-to-give-an-insulin-injection.html photo credit
- https://www.drwf.org.uk/news-and-events/news/%E2%80%98golden-rules%E2%80%99-insulin-injection-published-forum-injection-technique photo credit
- https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/assessment-skills/injection-technique-2-administering-drugs-via-the-subcutaneous-route-28-08-2018/ photo credit
- https://stock.adobe.com/in/images/insulin-injection-technique-in-diabetes-for-adults-and-children-depending-on-the-length-of-the-needle-anatomical-vector-illustration-in-flat-style-isolated-on-white-background/280266359 photo credit
- http://www.myhealth.gov.my/en/insulin-injection-technique/






Learning the right way to inject insulin makes such a difference to overall health. I’ve noticed how HIDPA supports people in understanding diabetes care better, which is so reassuring. It’s good to know there’s support available for those who need extra help managing their injections.
ReplyDelete